What is Kidney Disease?
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) occurs when kidneys are damaged and are less efficient at doing their job. CKD is called a “silent killer” because there are few symptoms, and by the time people realize they have a problem, much damage has already been done. High blood pressure and diabetes are the two leading causes of CKD. Heart disease, family history of CKD and obesity are other risk factors.
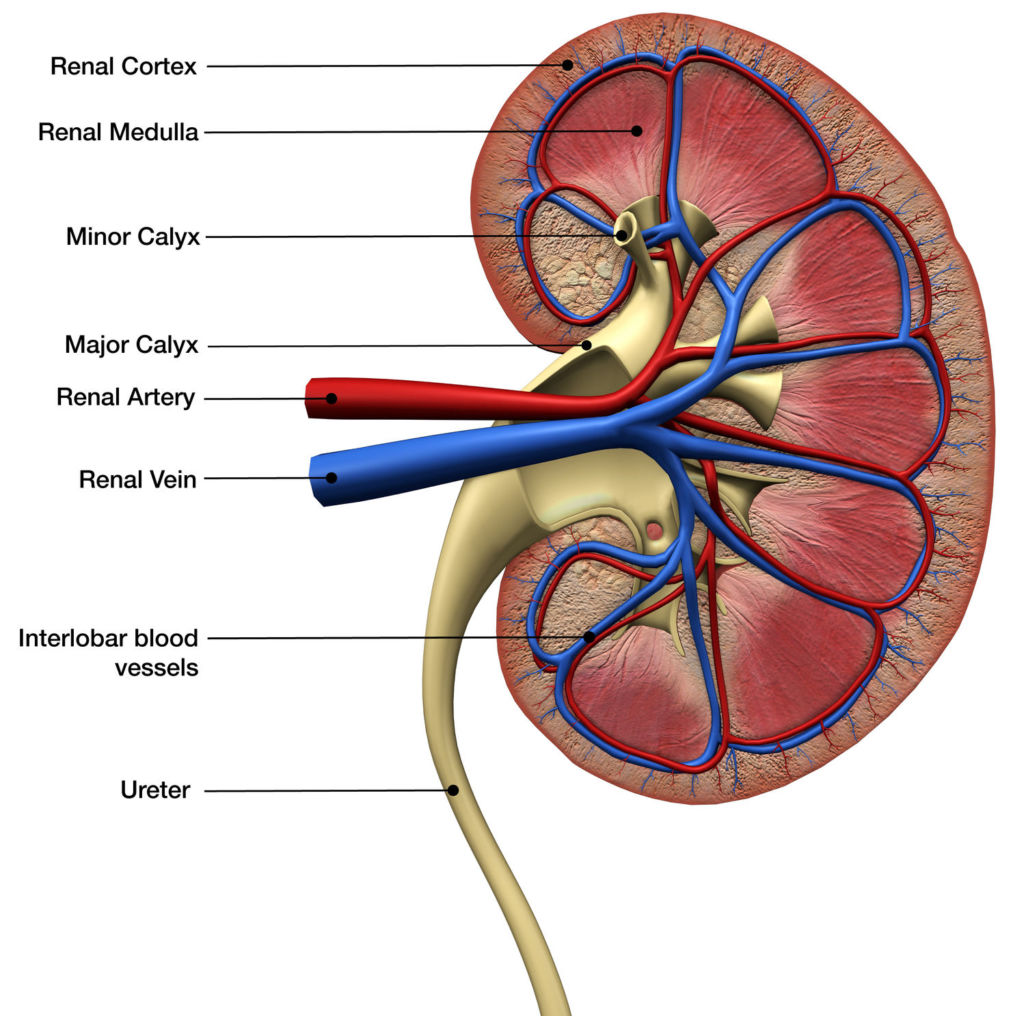
Role of Kidneys
Most people are born with two kidneys, which are each about the size of a closed fist. They are located in the middle back above the waist, with one on each side of the spine.
Kidneys serve an important role, as they are responsible for:
Kidney Failure
Kidney failure—also known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD)—is when kidneys are no longer able to do their job and the individual must either receive dialysis treatment or a kidney transplant in order to survive.